

Additional complexity in the meaning of matter comes from astronomical observations that began in the 1930s and that show that a large fraction of the universe consists of “dark matter.” This invisible material does not affect light and can be detected only through its gravitational effects. In the quantum view, elementary particles behave both like tiny balls and like waves that spread out in space-a seeming paradox that has yet to be fully resolved. The concept of matter is further complicated by quantum mechanics, whose roots go back to Max Planck’s explanation in 1900 of the properties of electromagnetic radiation emitted by a hot body. Einstein’s theory of gravitation, also known as his theory of general relativity (1916), takes as a central postulate the experimentally observed equivalence of inertial mass and gravitational mass and shows how gravity arises from the distortions that matter introduces into the surrounding space-time continuum. This transformation occurs, for instance, during nuclear fission, in which the nucleus of a heavy element such as uranium splits into two fragments of smaller total mass, with the mass difference released as energy. Einstein’s theory of special relativity (1905) shows that matter (as mass) and energy can be converted into each other according to the famous equation E = m c 2, where E is energy, m is mass, and c is the speed of light. Another universal property is gravitational mass, whereby every physical entity in the universe acts so as to attract every other one, as first stated by Newton and later refined into a new conceptual form by Albert Einstein.ġ,000,000,001 − 1,000,000,000 = 1 See all videos for this articleĪlthough basic ideas about matter trace back to Newton and even earlier to Aristotle’s natural philosophy, further understanding of matter, along with new puzzles, began emerging in the early 20th century. Image source: By Yeya18 CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons Solids have a fixed volume and shape. Youve probably learned a bit about solids, liquids, and gases at some point, so well begin with those.
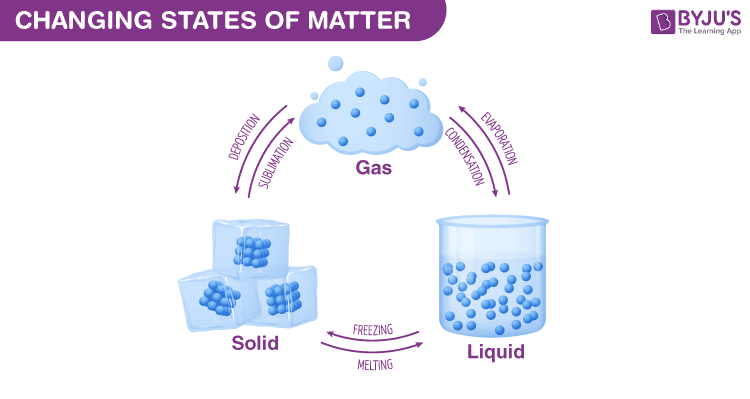
The mass of a body is a measure of this resistance to change it is enormously harder to set in motion a massive ocean liner than it is to push a bicycle. 5 What Are the Four States of Matter Matter can exist in four states (sometimes called phases): solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. However, all matter of any type shares the fundamental property of inertia, which-as formulated within Isaac Newton’s three laws of motion-prevents a material body from responding instantaneously to attempts to change its state of rest or motion. Less-clearly defined states of matter include plasmas, which are ionized gases at very high temperatures foams, which combine aspects of liquids and solids and clusters, which are assemblies of small numbers of atoms or molecules that display both atomic-level and bulklike properties. Solids, for example, may be divided into those with crystalline or amorphous structures or into metallic, ionic, covalent, or molecular solids, on the basis of the kinds of bonds that hold together the constituent atoms. These states can be further categorized into subgroups. At ordinary temperatures, for instance, gold is a solid, water is a liquid, and nitrogen is a gas, as defined by certain characteristics: solids hold their shape, liquids take on the shape of the container that holds them, and gases fill an entire container. The properties of a substance are the properties of a huge number of particles together.States of matter See all videos for this articleĭepending on temperature and other conditions, matter may appear in any of several states. The particles in the diagrams could be atoms, molecules or ions depending on the type of substance, egĪ single particle does not have the properties of the material it is part of. The model can be used to explain the physical properties of solids, liquids and gases. In condensed matter physics, a BoseEinstein condensate ( BEC) is a state of matter that is typically formed when a gas of bosons at very low densities is cooled to temperatures very close to absolute zero (273. It describes the arrangement, movement and energy of particles in a substance. The particle model represents particles by small, solid spheres. The three states of matter are solid, liquid and gas.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
